Exclusive Deals
Best Prices
Best Products
Fast Delivery
Exclusive Deals
Best Prices
Best Products
Fast Delivery
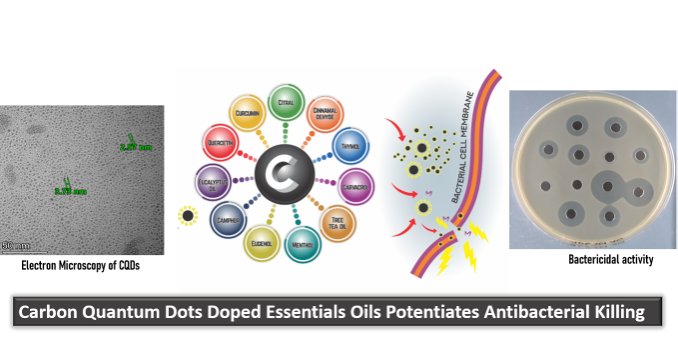
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) have unique properties that make them attractive for a range of biomedical and pharmaceutical applications enhancing the activity of natural compounds like essential oils. Binding CQDs to essential oils can potentiate (enhance) the bioactivity of these oils through several mechanisms.